 Etymology Etymology
- Scientific name derives from Latin Gmelina, in honor of Johann Gottlieb Gmelin (1709-1755), a German naturalist, and the Latin word elliptica, referring to the shape of the leaf blades. (15)
Botany
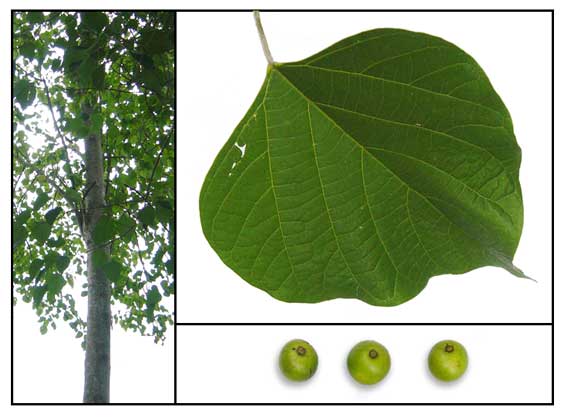
Taluñgud is a thorny, scrambling shrub
or small tree, 2 to 4 meters high, occasionally growing up to 8 meters. Leaves are elliptic or ovate,
4 to 9 centimeters long, 2 to 6 centimeters wide, blunt or slightly pointed at both ends,
wooly-felted or white-hoary on the lower surface, with minute green glands at the base, with entire or coarsely toothed margins.
Flowers are about 3.5 centimeters long, yellow, borne in terminal racemes up to
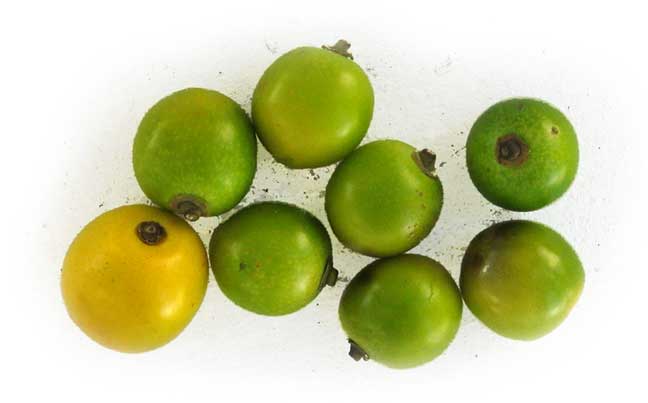
7.5 centimeters long, with rather large bracts. Calyx has 5 to 6 flat, green glands on one side, and small, toothed lobes. Corolla has a bell-shaped, 4-lobed mouth, and a very narrow tube below. The fruit is a drupe,nearly round, less than
2 centimeters in width, and yellow when ripe, with a watery flesh.
 Distribution Distribution
- Common in thickets and secondary
forests at low altitudes in Quezon Province in Luzon; and in Mindoro, Masbate, Panay, Guimaras, Negros, Cebu, Bohol, Mindanao, Basilan, and Bongao.
- Also occurs in Burma through Malaya to the Moluccas and the Palau Islands.
Constituents
- Study of aerial parts yielded 22 compounds from a chloroform extract, its prevailing compound, 1,2- benzenedicarboxylic acid, diisoctyl ester (31.22%); and 12 compounds from an ethanolic extract, its major constituent, monolinoleoylglycerol trimethylsilyl ether (38.51%).
Properties
- Bark and roots are demulcent
and alterative.
- Leaves are cathartic.
- Studies have suggested antidiabetic, anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, antimicrobial, antiproliferative properties.
Parts used
Leaves, fruit.
Uses
Folkloric
- Subanens in Zamboanga use poultice of leaves for stomach bloating. (12)
- In Malaya, plant is chiefly used as a poultice for headaches;
mixed with lime, used as poultice for swellings.
- Leaves used as cathartic.
- In Batavia, roasted fruit applied to foot itching caused by standing on stagnant waters.
- Infusion from fruit used as eye lotion.
- Fruit preserved in syrup and given in consumption.
- Juice from the fruit or leaves used for otalgia.
- Boiled leaves used for inflamed gums.
- Bark and roots used as demulcent and alterative.
- Leaves or roots applied to wounds.
- Leaves rubbed on gums to treat toothache.
- In Thailand, the bark of Uvaria spp. and Gmelina elliptica is used to treat nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
- In Indonesia, mashed berries mixed with berries of Solanum torvum
used as cure for beri-beri. (9)
- In Peninsular Malaysia, plant poultice used for headaches and swellings. (14)
- Roots are grated and shredded, mixed with urine of young children, and used to treat headaches, skin-related ailments, and rheumatism. Roots mixed with lime to treat swelling and anemia; applied to the scalp to prevent hair loss. Fruit pulp mixed with lime and garlic used on the body to treat dropsy. (15)
 Studies Studies
• Note: Revision of the scientific names and synonyms have separated Gmelina asiatica and G. elliptica as separate species. As some compilations list them as synonyms, the page will continue with studies on G. asiatica. I have not been able to find any study specific to G. elliptica. (G. Stuart)
• Hypoglycemic / Anti-Diabetic: Study of the alcoholic extract of root of Gmelina asiatica showed significant dose-dependent blood glucose reduction in normal and diabetic rats. The effect was compared with the drug tolbutamide. (2)
• Anti-Inflammatory: Study of the root powder in male albino rats showed the crude drug may exert anti-inflammatory activity by anti-proliferative, anti-oxidative and lysosomal membrane stabilization. (3)
• Antipyretic: Study showed the hexane and chloroform extract of G. asiatica roots showed significant antipyretic activity with no toxic activity. (4)
• Antimicrobial: The ethanolic extract of roots of G asiatica exhibited a broad spectrum of antimicrobial activity, particularly against E coli, P vulgaris and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (6)
• Antiproliferative / Anti-Breast Cancer: Study results suggest the efficacy of G. asiatica roots as antiproliferative agents on human breast cancer cells, supporting the hypothesis that plants containing lignans have beneficial effects on human breast cancer. (7)
Availability
- Wildcrafted. |



