 Botany Botany
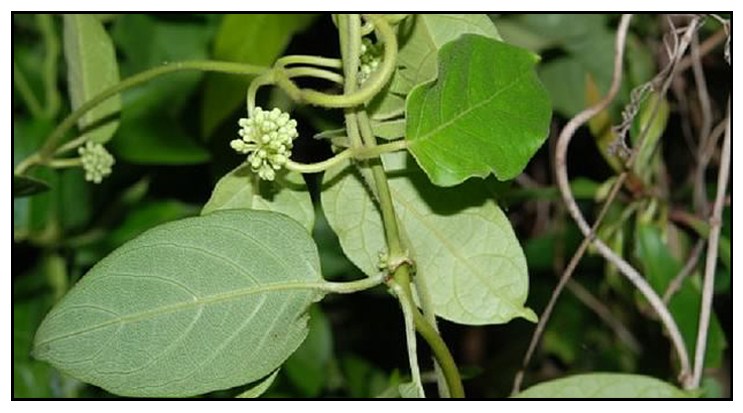
Payañgit is a twining, half-woody plant with very slender, smooth branches. Leaves are opposite, ovate to broadly ovate or somewhat rounded, 9 to 16 centimeters long, 5 to 10 centimeters wide, with pointed tip and heart-shaped base. Flowers are small, fragrant, yellowish green, borne in alternating clusters at the axils of the leaves, and 4 to 7 centimeters long. Fruit or follicle is lanceolate and somewhat angular, 5 to 8 centimeters long, and densely covered with hairs. Seeds are compressed and provided with profuse, silky-white hairs.
D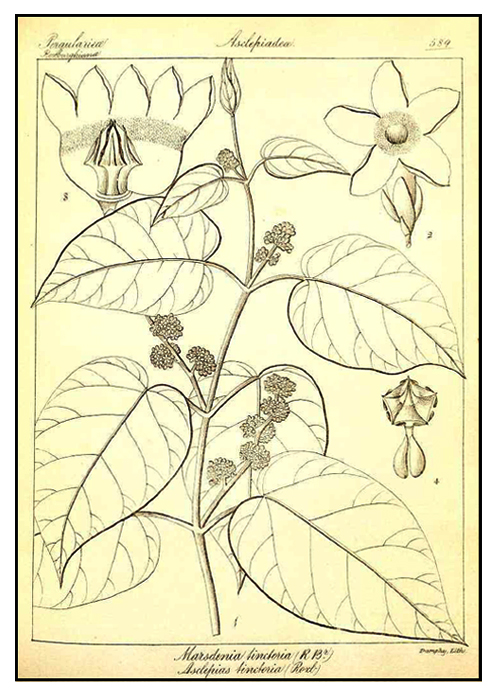 istribution istribution
- In secondary and primary forests at low and medium altitudes in Ilocos Norte, Abra, Bontoc, Benguet, Nueva Viscaya, Rizal, Laguna, Quezon, and Sorsogon Provinces in Luzon; and in Mindoro, Leyte, Panay, Mindanao, and Basilan.
- Also occurs in India to southern China and Malaya.
Constituents
- Stems yielded pregnane glycosides.
- Plant yields an indigo dye, for which it is sometimes grown.
- Study yielded seven constituents: lupenyl palmitate (1), lupenyl acetate (2), lupenone (3), lupeol (4), β-sitosterol (5), 5, 7-dihydroxy-2, 6, 8-trimethylchromone (6), and 2, 6-dimethoxybenzoquinone (7).
(10)
- Study isolated a new flavone kapitone (1) and three known compounds,
3,2’-dihydroxyflavone (2), 1-methylcyclobutene (3) and dimethyl isatoate (4).
(11)
- Root extract yielded alkaloid, flavonoid, terpenoid, steroid and polyphenol.
(see study below) (12)
Properties
- Its dye, like true indigo, is regarded as a good black dye for the hair.
- Considered stomachic.
- Studies have shown anti-implantation, abortifacient, antibacterial, oxytocic properties.
Parts used
Leaves.
Uses
Folkloric
- Used as antifertility and abortifacient.
-
Leaves sometimes used internally for stomach aches and vaguely diagnosed intestinal afflictions.
- Rubbed on the scalp to stimulate hair growth.
- The Sikkim healers of the Himalayas prescribed the leaf juice three times daily for stomach aches.(4)
- In Bangladesh, used by the Shautals to induce abortion.
- In Indonesia, used for contusion and fever.
(6)
- Among the Karbis of Assam, India, leaf paste applied twice daily for 3 days on dog bite wounds.
(16)
Others
- Dye: (1) In some parts of Southeast Asia, cultivated for its blue dye. (2) In Burma, green is produced by dipping threads that have been dyed yellow in a boiling decoction of the leaves and twigs of the creeping Marsdenia tinctoria. (3) Also considered a good black hair dye. (4) Used for tattooing. (5) Among the Karbis, M. tinctoria is the traditional source of the indigo dye, sibu. Tender leaves yield a blue color; when flowers and leaves are mixed, a red tinge against a blue background is produced (13).
- Ritual: A ritual plant in Sumatra, Indonesia, to expel bad spirits. (6)
- Fiber: Bark yields a fiber.
Studies
• Pregnane Glycosides: Study yielded three new pregnane glycosides, tinctorosides A-C, together with one known pregnane glycoside, stephanoside B, from the stems of M tinctoria. (1)
• Tinctoramine / Tinctoralactone / Antifertility / Abortifacient: Phytochemical screening yielded tinctoramine, a new steroidal alkaloid and tinctoralactone, a novel steroid. Both showed oxytocic, anti-implantation and abortifacient activities in mice and rats. (2)
• Oxytocic Principles: An alcohol extract and its alkaloidal fraction each showed oxytocic action on sensitized uterine horns of rat. The alkaloidal fraction was five times more active than the alcohol extract of oxytocin. (7)
• Antibacterial / Roots: Root extract of Marsdenia tinctoria showed antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. (see constituents above) (12)
• Indigo Dye / Leaves: Study evaluated four indigo plant varieties and other plants that give indigo dye. Results suggest Marsdenia tinctoria could be used to supplement indigo plants, with a yield of 0.025 g/100 g of indigo leaves (14)
• Decotion Alternative to Produce Indigo Tarum Areuy Dyes: Study reports on a faster extraction method by decoction method to produce indigo tarum areuy (Marsdenia tinctoria) dyes. (15)
• Antibacterial: In a study of 80% ethanol extracts from 20 Chinese herbal medicines collected in Yunnan Province screened for antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and MRSA, extracts from Marsdenia tinctoria dna Psychotria henryi were the most active, with mean IZDs=19.7 to 22.0 mm. Marsdenia tinctoria also showed inhibition against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Candia albicans. (17)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 istribution
istribution
