|
 Botany Botany
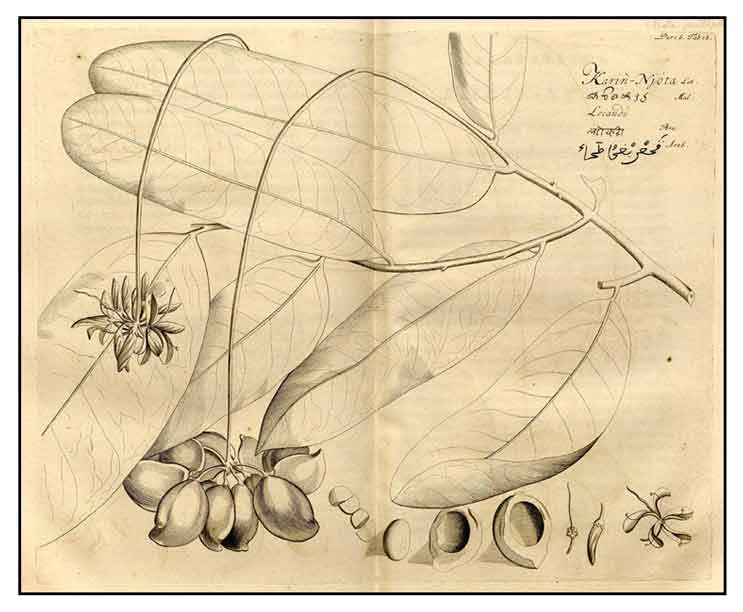
Manunggal is a tree, smooth
and growing to 10 meters high. Bark is pale and transversely cracked.
Wood is light yellow and soft. Leaves are simple, elliptic-oblong, about
20 centimeters wide. Flowers are numerous, bisexual, 4-parted, pinkish yellow, on
dense and pedunculated short-stalked umbels. Fruit is oval, about 6 centimeters long and 2.5 centimeters wide consisting of one carpet, flattened and keeled.
 Distribution Distribution
- Found in Cagayan,
Luzon; in Mindoro and Palawan; in Lanao, Mindanao; in forests at low
altitudes.
- Also found in India to Malaya.
Constituents
- Fixed oil, 33%; with triolein 87.7 %, triplamitin, 8.41 %, tristearin 3.89%, an alkaloid, a bitter principle and a glycoside, samaderin.
- The wood contains a bitter principle
similar to quassin.
- Study
on stems yielded four new quassinoids named samaderines X (1), Y (2), and Z (3), and indaquassin X (5), and a new C19 quassinoid glycoside, 2-O-glucosylsamaderine C (10), together with five known quassinoids, samaderines B (7), C (8), and E (4), indaquassin C (6), and simarinolide (9). (see study below) (1)
- Study of the seeds and bark yielded four quassinoids: indaquassin C, samaderins C, B and A. (see study below) (3)
- Methanol, chloroform, ethyl acetate, methanol and water extracts of bark yielded alkaloids (C, EA, M, W), flavonoids (M, W), triterpenoids (C, EA, M, W), tannins (M, W), phenols (M, W), carbohydrates (M, W), saponins (W), fats and fixed oils (C), phytosterols, (C, M, W). (see study below) (22)
Properties
- Bark is toxic with a bitter principle, as do the seeds.
- Bitterness attributed to flavanoids like quassinoids.
- Bark and wood considered febrifuge, tonic, stomachic and emmenagogue.
- Roots and fruits considered stomachic.
- Studies suggest antitumor, antifeedant, antiviral, anthelmintic, antioxidant, antimicrobial properties.
- Leaves reported termiticidal.
Parts used
Seeds, bark, and wood.
Uses
Folkloric
- Mixture of the powdered bark or wood scrapings in warm water or coconut oil used for fever.
- For rheumatism, seed is roasted, pounded, and applied over affected area.
- Leaves are bruised and applied over skin eruptions.
- Juice from pounded bark also used for skin diseases.
- Oil extracted from fruit kernels used for rheumatism.
- Leaf decoction used to relieve cough.
- Seeds worn around the neck for asthma prevention.
- Seeds used as emetic and purgative.
- Infusion of wood taken as a tonic, as a substitute for Quassia.
- Infusion of leaves used as insecticide, especially against white ants.
- In the Congo and Madagascar, used for malaria.
- In Ayurveda, Samadera indica pacifies vitiated vata, kapha, arthritis, edema, itching skin diseases, constipation, and general debility. (13)
- Macerated leaves, mixed with coconut oil, used for hair cleansing.(19) Also, to kill head lice.
- In Sri Lanka, mixture of powdered bark or wood scrapings in warm water or coconut oil used to treated fever. Roasted seeds are pounded and applied to areas of rheumatism. Bruised leaves applied over skin eruptions. Seeds worn around the neck to prevent asthma. (24)
Others
- Insecticidal / Termicidal: Leaf decoctions used to kill termites. Leaf infusion used as insecticide. (19)
- Wood: Soft wood used for making tool handles.
 Studies Studies
• Anti-Inflammatory / Antimalarial / Cytotoxicity: Study
on stems yielded four new quassinoids named samaderines X (1), Y (2), and Z (3), and indaquassin X (5), and a new C19 quassinoid glycoside, 2-O-glucosylsamaderine C (10), together with five known quassinoids, samaderines B (7), C (8), and E (4), indaquassin C (6), and simarinolide (9). Some of the compounds exhibited significant growth-inhibitory activity against cultured Plasmodium falcifarum. Compounds 1-8 exhibited in vitro toxicity against KB cells.
(1)
• Quassinoids: Quassinoids possess a wide spectrum of biological
activities. Reports have been made of its antimalarial, anti inflammatory
and antiviral properties and two studies have been published on quassinoids
anti-tumor activity, but thus far the compounds have been found to be
too toxic for clinical use.
(3)
• Quassinoids / Antifeedant: Study of the seeds and bark of Samadera indica yielded four quassinoids: indaquassin C, samaderins C, B and A. Indaquassin C was the most effective antifeedant. Samaderin C increased pupal duration and induced pupal mortality. (3)
• Mosquitocidal: Varied fractions and extracts, including Samadera indica leaf extracts significantly decreased the fecundity of mosquitoes and the hatchability of their eggs of C quinquefasciatus, A stephensi and Aedes aegypti. (4)
• Antibacterial: Study results indicated antibacterial activity, especially towards a single pathogen, Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Phytochemical screening yielded flavonoids, phenols and steroid. (5)
• Toxicopathology: Study evaluated evaluated the toxicopathology effect of gatep pahit stem extract fractionation of various extracts on mice liver and kidney at 100 mg kbw. Q. indica chloroform extract has the lowest level of damage to hepatocytes while hexane fraction caused the least damage in kidney tubular epithelium. The ethyl acetate showed the most epithelial damage. (8)
• Antimicrobial Topical Herbal Formulations: Study evaluated the toxicity of a methanolic extract of Samadera indica Gaertn. and its suitability for use in herbal formulations. The in-vitro antimicrobial study of the formulated ointment showed significantly strong activity against S. aureus, P. aeurginosa and C. albicans. Results suggest the formulated ointment and gel are safe and efficient formulations for topical delivery. (9)
• Antimicrobial / Antioxidant: Study evaluated the antioxidant and antimicrobial activity of methanolic extracts. Results showed significant activity against gram positive, gram negative bacteria, and Candida albicans. Antioxidant testing showed increased scavenging activity in a dose-dependent manner. (10)
• Polyherbal Antiseptic Ointment: An ointment, formulated using methanolic extracts of Azaridachta indica, Chromolaena odorata, Mimosa pudica, and Samadera indica, was evaluated for antibacterial and antioxidant activity. Results showed concentration-dependent increase in scavenging activity, the effect attributed to flavanoids and tannins. Antibacterial testing showed wound healing activity. Overall study showed an effective polyherbal antiseptic ointment. (11)
• Anthelmintic: Study of alcoholic and aqueous extracts from leaves were evaluated for anthelmintic activity against Rallietina spiralis and Ascaridia galli. The extracts showed significant dose dependent anthelmintic activity. (12)
• Antioxidant: Study evaluated various extract for antioxidant activity using DPPH, ABTS radical scavenging assay, FRAP, and DCF/AAPH assay. All methods showed prominent antioxidant activity although comparatively lower than standard Quercetin. (14)
• Anti-inflammatory Activity: Study evaluated the anti-inflammatory activity of Samadera indica by HRBC membrane stabilization. An ethanolic extract of S. indica showed significant anti-inflammatory activity. Diclofenac was used as standard. (16)
• Anti-inflammatory / Antioxidant / Leaves: Study of a methanol extract of Quassia indica leaves in Wistar albino rats showed significant in-vitro antioxidant activity by DPPH radical scavenging method and significant anti-inflammatory activity against carrageenan induced paw edema. (18)
• Hepatoprotective / Leaves: Study evaluated the potential hepatoprotective effect of methanolic extract of Quassia indica leaves in carbon tetrachloride induced liver injury in Wistar albino rats. Results showed hepatoprotective activity with restoration of increased level of serum biochemical markers and normalization of hepatic globular architecture. (19)
• Antimicrobial / Bark and Leaf: Study evaluated bark and leaf extracts of Quassia indica for antimicrobial activity against two strains of bacterial (E. coli and S. aureus) and fungi (A. niger and C. albicans). Results showed the leaf extract as an effective antibacterial and antifungal at concentration of 1000 µg/ml. (see constituents above) (22)
• Antioxidant / Bark and Leaf: Study evaluated methanolic extracts of bark and leaf for antioxidant property using varous assays. IC50s were ABTS (552.36, 1917), cH2O2 (566.89 and 1904.32), NO (956.75, 1711.74) and superoxide (235 and 506.68) for bark and leaf, respectively. (23)
• Antifungal / Phytovesicles Containing Triterpenoids: Study evaluated a novel phyto-vesicular formulation for an enhanced topical delivery of a methanol extract to treated skin infections. Chloroform 100% fraction of methanol extract of S. indica showed more activity against C. albicans and was positive for triterpenoids. The phytovesicle gel formulation showed enhanced skin permeability and antifungal activity and showed potential benefit for treating deep seated fungal infections. (25)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Herbs and extracts in the cybermarket.
|


![]()

