|
 Botanical snippet Botanical snippet
- Intsia bijga, ifit, is the official tree of the United States Territory of Guam.
Botany
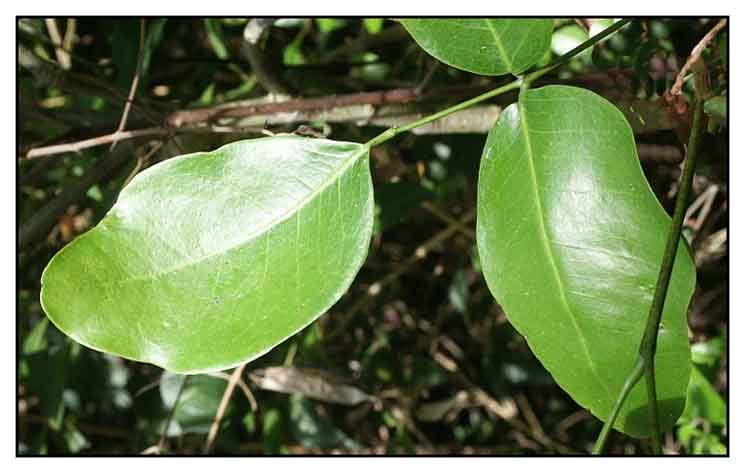
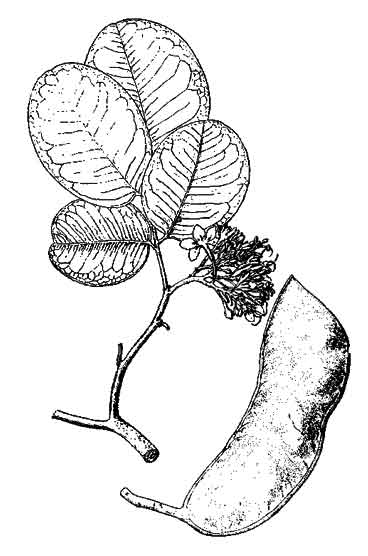
Ipil is a medium-sized, slow growing tree reaching a
height of 20 to 45 meters and a trunk of 0.5 to 5 meters. Mature trees have steep rounded buttresses.
Bark
is 5 to 8 millimeters thick, gray in color with an orange tinge. The inner bark is light
brown and mottled with brown specks. Leaves are alternate and simply
compound with usually two pairs of leaflets, 8 to 12 centimeters long and 5 to
8.5 centimeters wide. Flowers are fragrant, white or reddish, borne in panicles
6 to 10 centimeters long. Pods are oblong or pear-shaped, woody, tardily dehiscent, 10 to 25 centimeters long and 4 to 6 centimeters wide, with
3 to 9 orbicular seeds.
 Distribution Distribution
- Along the seashore,
and in some localities, in inland forests, from the Babuyan Islands and northern Luzon to Mindanao and Palawan.
- Also occurs in India, Burma, Thailand, Cambodia, Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, New Guinea to Australia and the Pacific Islands.
- IUCN listed as Vulnerable. (1998) (9)
Constituents
- Bark yields tannin.
- Wood yields a khaki-colored dye.
- Phytochemical screening of leaves yielded anthrones, flavonoids, glycosidic flavonoids, phenolic compounds, steroids, tannins, triterpenes, anthraquinones and coumarins.
- Study has shown robinetin as the main polyphenol of the heartwood of I. bijuga, together with 3,5,4'-tri and 3,5,3',4'-tetrahydroxystilbenes, dihydromyricetin myricetin, and narigenin (Hills and Yazaki, 1973). (11)
Parts
utilized
Leaves, bark, fruit.
Uses
Edibility
• Seeds can be eaten after careful preparation: soak in salt water for 3-4 days, and then boiled.
Folkloric
• Bark, which
contains tannin, used for diarrhea.
• Fruit used as laxative.
• Bark used for urinary conditions.
• In Fiji, decoction
of bark used for rheumatism, chills, diarrhea, muscle rigidity and rheumatoid
arthritis; mixed with the extracts of other plants, used for broken
bones. Juice of stems used for asthma.
• Decoction of leaves used when body is possessed by spirits.
• Mixed with other plant extracts, used for toothache and sore tongue. Also
used for scabies and headaches.
• Bark infusion given to women after delivery.
• In the Solomon Islands,
used to treat very dark urine caused by sorcery; also used for rheumatism,
diarrhea and dysentery.
• In Samoa, bark
used for treating enlarged lymph nodes.
• In Vanuatu, the
inner bark of Intsia bijuga, squeezed in coconut water, is taken as
a remedy for asthma. The leaves or inner bark are squeezed in salt water
and the solution is ingested for diabetes. (2)
• In Madagascar, women from Agnalazaha littoral forest use leaves for cough and placental appositioning. (12)
 Others Others
• Ritual: In Fiji, once considered a sacred tree. The traditional drinking bowl for yagona was made from the wood of the tree. Also, leaf decoction drank to rid the body of evil spirits.
• Wood: Known for its hard and durable wood; used for
timber, furniture making or carving craftwood. Durable against dry-wood termite, Cryptotermes cynocephalus the the subterranean termite Coptotermes curvignathus. (10)
• Dye: Wood yields a khaki colored dye. Fresh sap makes indelible stains on paper or cloth.
• Repellent: An insect repellent is made from the seeds.
• Poison: Seed oil repels stored products, tenebrionid pest
Studies
• Anti-trypanosomal: The
ethanol extract showed good and specific activity against Trypanosoma
cruzi. However, it also exhibited high cytotoxicity which might explain
its observed activity. Study has also suggested immuno-modulatory activity.
• Phytochemicals / Radical Scavenging Activity: In a study of four Philippine medicinal plants, phytochemical screening of Intsia bijuga revealed anthrones, flavonoids, glycosidic flavonoids, phenolic compounds, steroids, tannins and triterpenes. The tannins may justify its folkloric use for dysentery (leaves). I. bijuga showed lowest radical scavenging activity, with EC50 of 1846 µg/ml. (3)
• Cytotoxicity: On brine shrimp lethality assay, I. bijuga leaves had an LC50 value of 86.5 µg/ml. All crude methanol extracts of the four Philippine medicinal plants tested had 100% mortality to brine shrimp at 1000 µg/mL. (3)
• Anti-Ulcer / Leaves: Study evaluated methanol extracts of leaves of nine plants, including Intsia bijuga, for anti-ulcer activity using HCl-ethanol as ulcerogen. All extracts showed inhibitory activity with I. bijuga among those that showed more than 50% inhibition. (5)
• Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity: Xanthine oxidase inhibitors is a urate lowering agent, blocking the synthesis of uric acid, and used in the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout. Study evaluated the xanthine oxidase inhibitory activity of methanol leaf extracts of 10 plants, including Intsia bijuga. All the extracts inhibited the action of xanthine oxidase. (6)
Availability
Wildcrafted.
|


 Botanical snippet
Botanical snippet Distribution
Distribution  Others
Others

