 Botany Botany
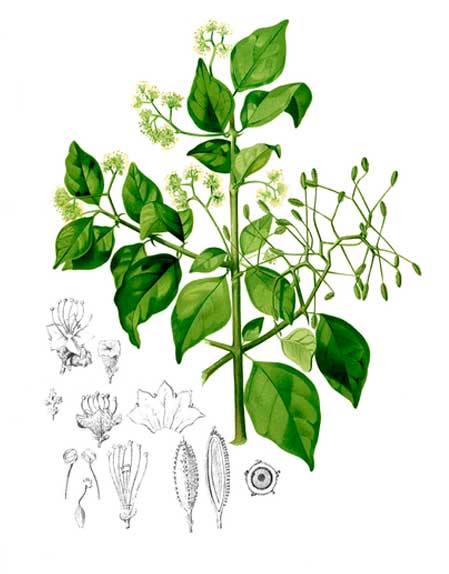
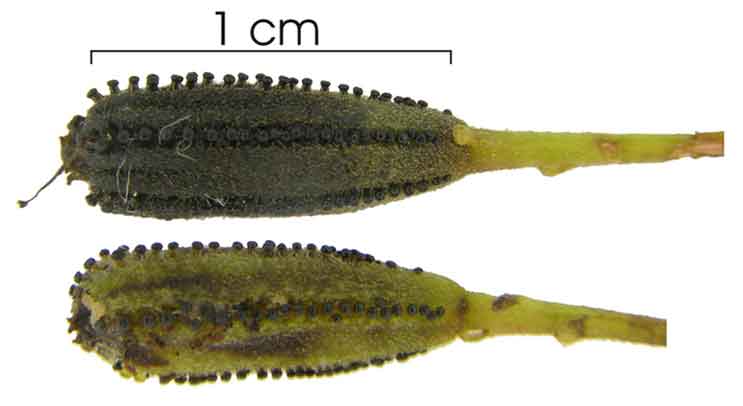
Digkit is a large, climbing shrub, smooth or slightly hairy, with pendulous branches, armed with solitary, axillary, recurved spines, which are about 1 centimeter long or less. Leaves are shining, ovate-oblong to elliptic, 6 to 10 centimeters long, with both ends pointed. Flowers are borne in axillary and terminal, peduncled, corymbose cymes. Male flowers are yellowish-white, bell-shaped, 4 to 5 millimeters in diameter. Female flowers are ovoid and obscurely toothed. Fruit is narrowly oblong or clavate, 5-ribbed, 7 to 14 millimeters long, viscid, with muricate ribs, with several rows of glands.
Distribution
- From northern Luzon to Mindanao, in thickets and open forests at low and medium altitudes.
- Pantropical.
- Found from subtropical America to Africa, to Burma, Indo-China, throughout Southeast Asia to New Guinea and northern Australia.
Constituents
- Studies have yielded alkaloids, glycosides, triterpenes, flavonoids, and phenolic compounds.
- Methanol extract of combined stem and root yielded three new chromones, pisonins A, B, and D, two new flavonoids, pisonivanone [(2S)-5,7,2′-trihydroxy-8-methylflavanone] and pisonivanol [(2R,3R)-3,7-dihydroxy-5,6-dimethoxyflavanone], one new isoflavonoid, pisonianone (5,7,2′-trihydroxy-6-methoxy-8-methylisoflavone) and five compounds first isolated from nature, namely, pisonins C, E, and F, pisoniamide, and pisonolic acid, together with 18 known compounds. (See study below) (5)
- Methanol extract of leaves yielded total phenolic content and antioxidant activities of 87.99 ± 0.87 mg GAE/g and 58.98 ± 0.01 QE/g, respectively. (see study below) (9)
- Study for flavonoids yielded rutin, myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, luteolin,
and orientin. (20)
Properties
- Studies have shown anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, anti-diabetic, anti-ulcer, antihyperlipidemic, hepatoprotective, antioxidant, analgesic, antipyretic, DNA-binging, anti-edematogenic, antitubercular properties.
Parts used
Bark and leaves.
Uses
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, decoction of fresh leaves used to wash scabies.
- Bark and leaves used as counterirritant for swellings and rheumatic pains.
- Juice mixed with pepper and other ingredients given to children suffering from pulmonary complaints.
- A popular medicinal plant in indigenous medicinal systems in India, Tibet, China and Korea.
- Used for treatment of scabies and as counterirritant for swellings and rheumatic pains.
- In India, used for scabies, syphilis, swelling. Bark paste used for rheumatism. Leaf decoction used for hepatitis. (19)
 Studies Studies
• Hepatoprotective / Antioxidant / CCl4-Toxicity: An ethanol extract showed a remarkable hepatoprotective and antioxidant properties of P. aculeata against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Silymarin was used as standard. (1)
• Anti-Tumor: Study on the ethanol extract of P. aculeata leaves on Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma in mice was shown to possess significant dose-dependent anti-tumor activity. (2)
• Hepatoprotective / Rifampicin and INH-Induced Hepatotoxicity / Leaves: Methanolic extract of leaves showed a remarkable hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity against rifampicin- and isoniazid-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Silymarin was used as standard drug.(3)
• Hepatoprotective / Paracetamol-Induced Toxicity: Plant extract showed remarkable hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity against paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity as evidenced by return of significantly altered serum marker enzymes to near normal levels. The activity was comparable to standard drug silymarin. (4)
• Antitubercular Chromones and Flavonoids: Study yielded three new chromones, pisonins A (1), B (2), and D (4); two new flavonoids, pisonivanone (7) and pisonivanol (8); one new isoflavonoid, pisonianone (9); and five other compounds, pisonins C (3), E (5), and F (6), pisoniamid (10) and pisonolic ac (11), together with 18 known compounds. Isolates 2, 7, 14, 16, and 19 exhibited antitubercular activities (MICs ≤ 50.0 µg/mL) against Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv in vitro. (see constituents above) (5)
• Antitumor / Leaves: Study evaluated the antitumor activity of a methanolic extract of leaves on Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma (EAC) in mice with tumor induced by intraperitoneal injection. Results showed dose-dependent increase in survival time and inhibition in weight gain of the tumor bearing mice. (8)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant / Analgesic: Study evaluated a methanol extract of P. aculeata leaves for analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. Results showed significant (p<0.001) inhibition of paw edema and protective effect against hypotonic solution and heat induced hemolysis. The ME also showed inhibition of acetic acid induced writhing and late-phase formalin-induced nociception. The extract showed significant in vitro antioxidant activity and lipid peroxidation inhibition effect. Observed biological activities could be correlated with the flavonoid and phenolic compounds in the extract. (see constituents above) (9)
• Antiulcer / Leaves: Study evaluated various leaf extracts for antiulcer activity in a pylorus ligation induced gastric ulcer model in albino rats. Results showed significant antiulcer activity at dose level of 200 mg/kg. Ranitidine was used as standard. (10)
• Antidiabetic / Leaves: Study evaluated ethyl acetate and ethanolic extract of leaves on alloxan-induced diabetes in rats. Both extracts exhibited significant hypoglycemic effect, together with reduction in BUN, serum creatinine, and serum cholesterol. (11)
• Hepatoprotective / Antioxidant / Thioacetamide-Induced Hepatotoxicity: P. aculeata extract exhibited remarkable hepatoprotective and antioxidant activities against TAA-induced hepatotoxicity in male wistar rats. Silymarin was used as standard drug. (12)
• Acute and Subacute Toxicity Testing: Study evaluated a methanolic extract of leaves for acute and subacute toxicity. On acute toxicity stud, it was found to be safe, with no mortality even at high dose of 2 g/kg. In subacute toxicity study, at doses of 100, 250, and 750 mg/kg for 28 days, no mortality occurred, and hematologic parameters remained within normal range. (13)
• Antihyperlipidemic / Antidiabetic: Study investigated the antihyperlipidemic and antidiabetic activity of alcoholic extract of PA in albino wistar rats with hyperlipidemia induced by Triton X and diabetes by streptozotocin. Results showed good antidiabetic activity and antihyperlipidemic activity. (15)
• Antiedematogenic / Toxicity Study / Stems: Study investigated the antiedematogenic activity of crude extract and derived fractions from stems of P. aculeata. Crude methanolic extract and all fractions, especially hexane and chloroform, showed inhibitory activity of mice ear edema induced by croton oil. On acute toxicity testing, there was no death or change in behavioral parameters, suggesting non-toxicity of the extract. (16 )
• Antipyretic / Bark: Study evaluated ethanolic and aqueous extracts of bark of Pisonia aculeata for antipyretic activity in Brewer's yeast induced pyrexia in rats. Results were compared to standard drug paracetamol. (17)
• DNA Binding / Anticancer Activity: Anticancer drugs interact with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) in various ways, such as intercalation, non-covalent groove binding, cleaving, nucleoside-analog incorporation, covalent binding/cross-linking. As a results, the thermodynamic stability and functional properties of DNA change. This study of P. aculeata methanolic extract of leaves. The MPA has been shown to possess DNA-binding abilities. Study reports on the mechanism of action and its potent activity against various tumor cell lines. (18)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()



 Botany
Botany
