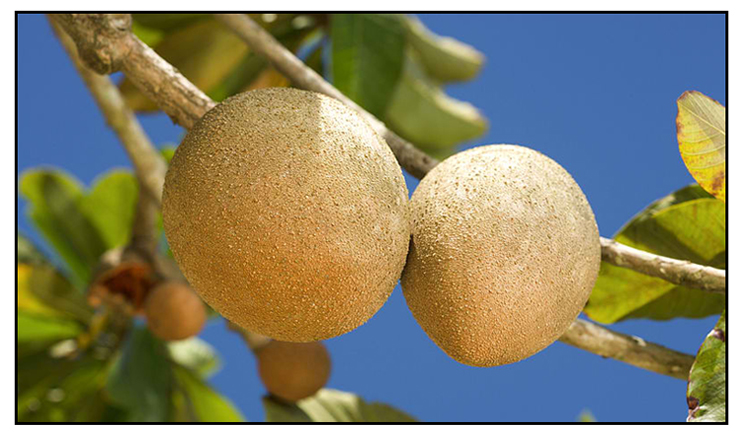
 Botany Botany
Chico-mamei is a large tree with a thick trunk and stout branches, growing to a height of 15 meters. Leaves are clustered toward the ends of the branchlets, oblanceolate, 12 to 30 centimeters long, 4 to 7 centimeters wide, smooth, light green above, pale brownish beneath, and pointed at both ends. Flowers are white, 6 to 12 in the axils of fallen leaves, and measures 10 to 12 millimeters across. Sepals are ten, densely imbricated in several series. Corolla has five lobes. Fruit is oblong or ovoid, 7.5 to 15 centimeters long, with a thick, russet-brown skin and firm, reddish flesh which is very sweet and pleasant tasting.
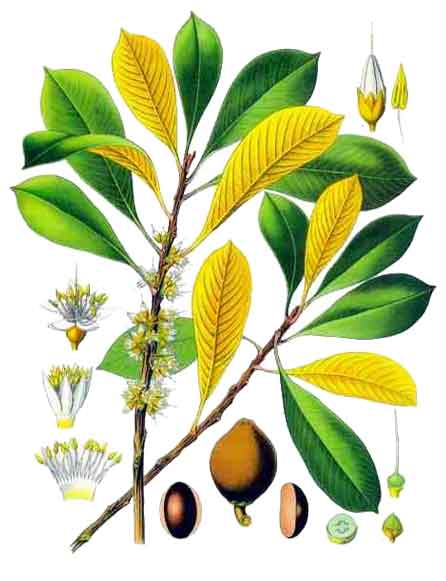 Distribution Distribution
- Planted in Luzon, particularly the Cavite and Laguna Provinces.
- Introduced from Mexico by the Spaniards.
- Native to Mexico, Nicaragua, Puerto Rico.
Constituents
- Seeds contain amygdalin; a gutta percha-like substance, fatty oil with stearin and glyceride.
- Bark is reported to yield hydrocyanic acid.
- Fruits yielded new carotenoids, cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide, 3′-deoxycapsanthin-5,6-epoxide, and cryptocapsin-5,8-epoxides. (5)
- Analysis of oil from fruits revealed benzaldehyde, hexanal, and palmitic acid.
- Nutrient analysis per 100 g of edible portion yielded
114.5 calories, 55.3-73.1 g moisture, 0.188-1.97 g protein, 0.09-0.25 g fat, 1.41-2.97 carbohydrates, 1.21-3.20 g fiber, 0.89-1.32 g ash, 28.2-121.0 mg calcium, 22.9-33.1 mg phosphorus, 0.52-2.62 mg iron, 0.045-0.0.665 mg carotene, 0.002-0.025 mg thiamine, 0.006-0.046 mg riboflavin, 1.574-2.580 mg niacin, 8.8-40.0 mg ascorbic acid; and amino acids, 19 mg tryptophan, 12 mg methionine, 90 mg lysine. (8)
- Study of ripe fruits of red mamey (Pouteria sapota) yielded new carotenoids, cryptocapsin-5,6-epoxide, 3′-deoxycapsanthin-5,6-epoxide, and cryptocapsin-5,8-epoxides. (9)
- Study of mamey sapote defatted meal (MSDM). MSDM yielded a protein content of 240.6 g/kg with glutelins (57.25%), prolamins (18.65%), albumins (17.85%), and globulins (6.25%).
(see studies below) (12)
- Nutrient analysis of far mamey (sapote) per 100 g: (Proximates) water 64.87 g, energy 124 kcal, protein 1.45 g, total fat 0.46 g,
carbohydrate (by difference) 32.10 g, total dietary fiber 5.4 g, total sugars 20.14 g; (Minerals) calcium 18 mg, iron 0.78 mg, magnesium 11 mg, phosphorus 26 mg, potassium 454 mg, sodium 7 mg, zinc 0.19 mg; (Vitamins) vitamin C 23.0 mg, thiamin 0.013 mg, riboflavin 0.116 mg, niacin 1.432 mg, vitamin B6 0.720 mg, vitamin A 7 µg, vitamin E 2.11 µg; (Lipids) total saturated fatty acid 0.169 g, total monosaturated FA 0.102 g, total polyunsaturated FA 0.097, trans FA 0, cholesterol 0. (15)
Properties
- Considered emetic, diuretic, anthelmintic.
Parts used
Sap, seeds, fruit pulp.
Uses
Edibility
Fruit is pleasantly sweet tasting.
Folkloric
- Aztecs reported to use it for dressing the hair to keep it soft and to prevent dandruff. Seed coat used as a remedy for epilepsy.
- In Costa Rica, used for curing colds.
- Sap of tree said to be emetic and anthelmintic.
- Seeds used as diuretic.
- Pulverized seed is drunk with wine to cure gravel and heart affections.
- Powdered seeds used as remedy for renal colic.
- In Antilles, fruit pulp is used as sedative cataplasm. Also, infusion of bark used as pectoral.
- In Santo Domingo, seed kernel oil used as skin ointment and as hair dressing to hair loss. Oil is used as sedative for eye and ear problems. Seed residue after oil extraction used as poultice for painful skin afflictions. (8)
- In Cuba, seed infusion used as eyewash. In Mexico, pulverized seed coat use for heart problems. Aztecs use it for epilepsy. In Costa Rica, bark and leaf decoction used in treatment of atherosclerosis and hypertension. Milky sap used to remove warts. (14)
Others
- Seed oil: Seeds and seed oil used in the manufacture of soap, perfumery, cosmetics, and pharmaceutical products. In olden times, used to fix colors of painted crafts and handicraft. (8)
- Apiculture: Nectar of flowers gathered by honeybees. (14)
- Dye:
Dye used in olden times to color gourds and handicraft. (14)
- Wood: Suitable for use in furniture and cabinetry work. (14)
Studies
• Antioxidant / Radical Scavenging Activities: Ethyl acetate fraction of methanol extracts exhibited radical scavenging and antioxidant activities.
• Trypanocidal: The methanol extract from P sapota stems exhibited trypanocidal activity in vitro against epimastigote form of Trypanosoma cruzi.
• Lucumin and Related Glycosides: Three aromatic glycosides, lucumin, lucuminamide and lucuminic acid, were isolated from the seeds of Calocarpum sapota. (2)
• Antioxidant: Study on fresh fruits of three Pouteria species, P sapota, P viridis, and P campechiana, yielded seven polyphenolic antioxidants: (+)-gallocatechin, (+)-catechin, (−)-epicatechin, dihydromyricetin, (+)-catechin-3-O-gallate, and myricitrin. (3)
• Comparative Antioxidant Activities: Study compared the antioxidant activities of M. zapodilla, C. caimito, and Pouteria sapota. All three have antioxidant properties. On -OH screening, P. sapota was second; on DPPH and ABTS assays, P sapota was third. (6)
• Antioxidant / Phytoconstituents / Fruit: Study evaluated the antioxidant and phytochemical profile of mamey fruit. Hydrophilic extracts showed higher antioxidant capacity than the lipophilic portion. Total soluble phenols content was 28.5 mg GAE/100 g fw, with p-hydroxybenzoic acid as main phenolic content. Total carotenoid content was 1127.9 µg/100 g fw, with ß-carotene as main constituent, in addition to lutein and violoxanthin. δ-tocopherol was 360.0 µg/100 g fw. (10)
• α-Amylase Inhibitors / Kernel: Study reports on the extraction of α-amylase from kernel of Pouteria sapota. Results showed 95.8% pancreatic α-amylase inhibitory activity. TLC analysis reported the presence of rutin and quercetin related flavonoids in the kernel. (11)
• Potential Source of High Purity Protein Isolate: Study evaluated the proximate composition and properties of protein fractions in a mamey sapote defatted meal (MSDM). MSDM yielded a protein content of 240.6 g/kg with glutelins (57.25%), prolamins (18.65%), albumins (17.85%), and globulins (6.25%). Results suggests the MSDM is suitable material for the production of a high-purity protein isolate with a potential as ingredient in meat or bakery products. (12)
• Inactivation of Polyphenol Oxidase by Microwave Treatment: Polyphenol oxidase (PPO) is the enzyme responsible for quality loss in most fruits and vegetables, including mamey fruit (Pouteria sapota) which undergoes rapid quality decay through PPO activation. Inactivation of PPO in situ may be achieved by chemical or thermal treatment. Study reports on microwave treatment (MT) as an effective way to completely inactivate PPO without causing any significant damage to fruit tissue and shape with preservation of color, flavor and taste. (13)
• Silver Nanoparticles / Antidiabetic / Leaves: Study reports on the green synthesis of AgNPs from aqueous leaf extracts of P. sapota. The aqueous leaf extract of P. sapota and AgNPs exhibited efficient antidiabetic activity in STZ induced diabetic rats. (16)
• Functional Protein Isolate / Seed: Study evaluated a mamey sapote deffated meal (MSDM) for proximate composition and functional properties. The MSDM showed a protein content of 240.6 g/kg with protein components of glutelins (57.25%), prolamins (18.65%), albumins (17.85%), and globulins (6.25%). A mamey protein isolate (MSPI) showed a protein content of 950.9 g/kg and an in vitro digestibility of 73.6%. Results suggest the MSDM is a suitable material for the production of high-purity protein with potential as ingredient in meat or bakery products. (17)
• Quercetin / Antioxidant / Anticancer / Fruits: Study isolated quercetin from P. sapota fruit. The quercetin and P. sapota plant extract was assessed by MTT assay for effect on Human Breast cancer (MCF-7) cell lines and antioxidant activity by DPPH method. The isolated compound exhibited time- and dose-dependent killing capabilities in various tumor cell lines. Cell death was via apoptosis. (18)
Availability
Wild-crafted.
|

![]()




 Distribution
Distribution