 Botany Botany
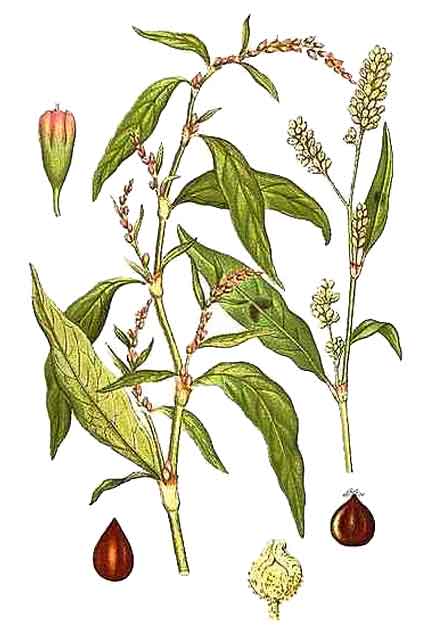
Buding is a smooth, rather robust annual, with tufted or shortly creeping roots. Stems are erect, while the branches are ascending, rather stout and leafy, 30 to 45 centimeters high, often glandular. Nodes are often swollen. Leaves are lanceolate or oblong-lanceolate, up to 7.5 centimeters long. Racemes are flexuous, leafy at the base, threadlike, decurved and interrupted. Flowers are pinkish. Nuts are usually three-sided.
 Distribution Distribution
- In the Benguet Province of Luzon, in open wet places, along streams, in old rice paddies, etc., at altitudes of 1,200 to 2000 meters.
- Occurs in warmer parts of the world.
Constituents
- Seed contains polygonic acid and tannin.
- Leaves contain an essential oil, malic acid and phytosterine.
- Rootstock yield an essential oil, oxymethyl-anthraquinone.
- Screening of ethanol extract yielded alkaloids, flavonoids, saponins, tannins, terpenoids, and steroids.
(see study below) (20)
- Leaves yield 7.5% protein, 1.9% fat, 8% carbohydrate, 2% ash. Also contains rutin.
- Study of whole plant yielded one new drimane-type sesquiterpenoid, 3 β-angeloyloxy-7-epifutronolide (1), and one new natural product, polygonumate (2), along with six known drimane-type sesquiterpenes-- [dendocarbin L, (+) winterin, (+) fuegin, changweikangic acid A, futronolide, and 7-ketoisodrimenin. (14)
- Various extracts and fractions yielded flavonoids such as (+)-catechin, (−)-epicatechin, hyperin, and isoquercitrin; isorhamnetin, kaempferol, quercetin, quercitrin, rhamnazin and rutin; drimane-typed sesquiterpenes, such as 3-β-angeloyloxy-7-epifutronolide, 7-ketoisodrimenin, changweikangic acid A, dendocarbin L, (+)-fuegin, futronolide, polygonumate, and (+)-winterin; phenylpropanoid esters, including hydropiperosides A and B, and vanicosides A, B and E; and phenolic acids, such as caffeic acid, chlorogenic acid and ρ-coumaric acid. (16)
Properties
- Considered anti-inflammatory, astringent, carminative, contraceptive, diaphoretic, diuretic, emmenagogue, stimulant, stomachic, styptic.
-
Juice considered diuretic, carminative and anthelmintic.
- Root is bitter, tonic, and stimulating.
- Studies have suggested antioxidant, antibacterial, antifungal, anthelmintic, cytotoxic, anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive, antifertility, anti-obesity and neuroprotective properties.
 Parts used Parts used
- All plant parts.
Uses
Edibility
- Leaves and stems are edible, raw or cooked.
- Seeds
made into a peppery condiment as substitute for pepper.
-
Young seeds used as salad garnish.
- In Japan, young shoots used as spice and garnish with raw fish (sashimi). (16)
- Water or ethanol extracts used as food additive to preserve pickles, dressing and cooked food. (16)
Folkloric
- In China, juice is used for itches; also as diuretic, carminative and anthelmintic.
- Root used as tonic and stimulant.
- Decoction of whole plant used for diarrhea, dyspepsia, hemorrhoids, and excessive menstrual bleeding.
- Bruised leaves used as poultice and cure for toothache.
- Used to regulate menstrual irregularities.
- Used for treatment of obesity.
- Among Russian peasant, used as hemostatic.
- Used in all cases of intestinal hemorrhage (pulmonary, gastric, hemorrhoidal, uterine) and used as sedative.
- In the United States, once used as an emmenagogue.
- In Assam, women used the roots for fertility control: Dried root powder used for termination of pregnancy; continuous use for more than a year reported to cause permanent sterility. (16)
- In Bangladesh, leaf juice used for menstrual pain and leaf paste to stop bleeding. (16) Used for the treatment of insomnia, depression and neurodegenerative illnesses. (27)
- In Vietnam, stems and leaves used for snake bites; also as diuretic and anthelmintic. (16)
- In Bangladesh, leaves used to treat rheumatic pain, gout, skin diseases (scabies, ringworm), abscesses, snake, dog, and insect bites. (17) Juice of leaves used for headaches, pain, toothache, liver enlargement, gastric ulcers, dysentery, dysmenorrhea and loss of appetite. (24)
- In Malaysia, decoction consumed to heal stomach ache; also used to treat dandruff. (20)
- In the Himalayas, leaf juice used in uterine disorders. The tribal people of Tripura and Bangladesh use the plant to treat headaches: the leaves are crushed with ten black peppers and taken through the nose. In Assam, leaf juice used for pains. Leaf extract applied externally to scabies. (29)
Others
- Dye: Yields a yellow dye used as traditional fabric dye. (29)
- Repellent: Dried plants used as insect repellent and to protect clothes. Leaf extract is sprayed against crop pests. (29) Juice used to keep flies off livestock injury.
- Fish poison: Used to stupefy fish. (29)
 Studies Studies
• Hydropiperoside / Antifertility Activity: Study of methanol extract yielded a novel coumaryl glycoside, hydropiperoside, with other known compounds and an unidentified lactone possessing antifertility activity. (1)
• Antioxidant Flavonoids: Study isolated ten flavonoid compounds from the dried leaves of P. hydropiper. The isolated flavonoids were shown to possess strong antioxidative capabilities. The most powerful was galloyl quercitrin. (2) Study showed good antioxidant activity on ORAC assay. (20)
• Antibacterial / Antifungal: Study of root extract showed significant antibacterial activities against four gram-positive (B subtilis, B megaterium, S aureus and E aerogenes) and four gram-negative (E coli, P aeruginosa, S typhi and S sonnei) bacteria, with antifungal activity against A fumigatus, A niger, A flavus, C albicans, Rizopus oryzae and T rubrum. (3)
• Lens Aldose Reductase Inhibition: Sulfated flavonoids in Polygonum hydropiper showed potent inhibition against lens aldose reductase. Among the flavonoids, the most potent was isorhamnetin 3,7-disulfate. (4)
• Antifertility: Study of the methanolic extract of root showed anti-fertility activity in female albino rats. The estrous cycle of the extract treated rats became irregular resulting in failure of gestation. Results suggest the root of PH contains steroidal / estrogenic compounds which affect female reproduction in rats. (6)
• Insecticidal: Study of 5 kinds of Polygonum hydropiper organic solvent extracts showed the ethyl ether extract to have the strongest insecticidal effect. The insecticidal substance was identified as eugenol. Eugenol showed to have stomach toxicity and contact action; it suppressed AchE and GST activity. (7)
• Tyrosinase Activity Inhibitor: Study isolated taxifolin, a tyrosinase inhibitor from the sprout of Polygonum hydropiper. Compared to cosmetic agents arbutin and kojic acid, taxifolin's tyrosinase inhibitory effect was equal to the latter, more than the former. (8)
• Cytotoxic Activity: Study showed cytotoxic activity, yielding cytotoxic compounds soluble in both water and ethanol. Results suggest a therapeutic potential in antitumor therapy. (11)
• Estradiol-like Effects: In a study of crude extract of roots , P. hydropiper mimics the effect of estradiol-17ß in the uterine protein profiles of adult female albino rats. (12)
• Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Study of methanol extract of Polygonum hydropiper showed strong anti-inflammatory activity. There was dose-dependent suppression of release of nitric oxide (NO), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-a, and prostaglandin (PGE2) IN RAW264.7 cells and peritoneal macrophages stimulated by lipopolysaccharide. (13)
• Phytoremediation / Nitrogen and Phosphorus: Study showed the mining ecotype (ME) of P. hydropiper removed as high as 87.47% of total nitrogen and 97.63% of total phosphorus. Results show a theoretical basis for use of P. hydropiper for N and P removal from livestock wastewater and presents as a promising species for the phytoremediation of eutrophic waters. (15)
• Antinociceptive / Leaves: Study evaluated the antinociceptive activity of methanol extract of leaves in both heat- and chemical induced pain models in mice. Results showed significant antinociceptive activity with both central and peripheral mechanisms. Pretreatment with naloxone significantly reversed the antinociceptive produced by the MEPH suggesting involvement of the opioid system. (17)
• Antimicrobial / Insecticidal: Crude extracts of P. persicaria showed significant activity against E. coli. A leaf extract showed significant activity against A. niger and moderate activity against A. flavus, H. maydis, and A. solani. It showed insecticidal activity against T. castaneum, S. oryzae, R. dominica and C. analis. (18)
• Anthelmintic / Antiproliferative / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated aerial parts of Persicaria hydropiper for anthelmintic and antiproliferative activity. Results showed in vitro anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma. Study also showed in vivo antiproliferative activity against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma with significant (P>0.05) decrease in tumor weight, increase life span, and reduced tumor cell growth. (19)
• Anti-Obesity / Quercetrin / Inhibition of Differentiation of Adipocyte 3T3-L1 Cells: Evidence suggests Wnt/ß-catenin pathway can potentially control adipogenesis related to obesity. Study screened eleven plant extracts activating the Wnt/ß-catenin signaling reporter gene. Study showed the isoquercitrin in P. hydropiper suppresses the adipogenesis of 3T3-L1 cells via inhibition of Wnt/ß-catenin signaling. P. hydropiper and isoquercetrin may have potential as therapeutic agents for obesity and its associated disorders. (22)
• Insect Deterrent Drimanes / Drimenol Synthase and Drimenol Oxidase / Cinnamolide: Study isolated a drimenol synthase (PhDS) and a cytochrome P45) drimenol oxidase (PhDOX1) from P. hydropiper. In agro-infiltration in Nicotiana bethamiana leaves, drimenol was converted into cinnamoide and other drimenol derivatives. In vitro assays showed conversion from drimenol to drimendiol which was further oxidized and converted to cinnamolide. Purified cinnamolide was showed to be an effective deterrent against both whitefies and aphids with ED50 of about 200-400 µg g-1 fresh weight. (23)
• Antioxidant / Antibacterial: In a study of five Malaysian herbal extracts,P. hydropiper showed high antioxidant and antibacterial activities. It showed the highest antioxidant activities in FRAP and ORAC assays with 1676.67 mM TE/g EW and 11.20 mmol TE/g EW, respectively. (see constituents above) (20)
• Antihyperglycemic / Antinociceptive / Leaves: Study of various doses of ethanolic leaf extract of P. hydropiper in glucose-loaded mice showed significant reduction of blood glucose levels by 48.8% to 52.2% (p<0.05) compared to standard glibenclamide with 42.1% reduction. In antinociceptive activity testing, there was reduction of abdominal writhings by 14.10 to 41.02% compared to standard drug Aspirin. Brine shrimp naupili toxicity testing showed LC50 of 16.22 µg/ml, compared to control. (24)
• Xanthine Oxidase Inhibitory Activity / Antioxidant: Study evaluated methanol extract fractions for total phenolic content and antioxidant activity by DPPH, ferric thiocyanate and XO inhibition assays. Butanol and EA fractions showed higher phenolic content of 224.38 and 68.95 mg GAE/100g dry extract, respectively. Both showed DPPH radical scavenging activity with IC50 of 28.61 and 25.55 µg/ml. Both fractions inhibited xanthine oxidase activity with IC50 of 28.72 and 165.25 µg/ml. (25)
• Antimicrobial / Weak Antimalarial Activity: Study of two crude extract and two fractions from Polygonum hydropiper was evaluated for antimicrobial and antimalaria activity. Results showed weak antimalarial activity. Antimicrobial testing showed activity against Aspergillus fumigatus and mild activity against K pneumoniae, E. coli and C. neoformans. (26)
• Sedative and Anxiolytic / Leaves: Study of methanol extract of leaves of Persicaria hydropiper in mice showed sedative and anxiolytic effects. Sedative effect was evaluated using open field hole cross, rota rod and thiopental sodium-induced sleeping time , while anxiolytic activity was evaluated using elevated plus maze, light-dark box, hole board and marble burying test. (27)
• Larvicidal against Ae. aegypti / Dengue Fever Vector: The larvicidal efficacy of nine medicinal plants collected from Western Ghats, india, was assessed against fourth instar larvae of Aedes aegypti. The larvicidal assay was done according to WHO standard protocol with acetone, methanol, petroleum ether, and water extracts. Two of nine, Persicaria hydropiper and Plectranthus hadienses showed significant larvicidal efficacy with LC50s of 489.278 Mg/L and 414.746 Mg/L, respectively, against 4th instar larvae of the dengue fever vector. Results suggest the plants has potential as a natural insecticide for mosquito control programs. (28)
Availability
- Wild-crafted.
- Dried herbs in the cybermarket.
|

![]()




 Distribution
Distribution
 Studies
Studies 