|  General
info General
info
- Brunfelsia is a genus of flowering plants in the family Solanaceae, comprising about 50
species.
- Linnaeus named the genus for early German herbalist Otto Brunfels
(1488-1534). (9)
Botany
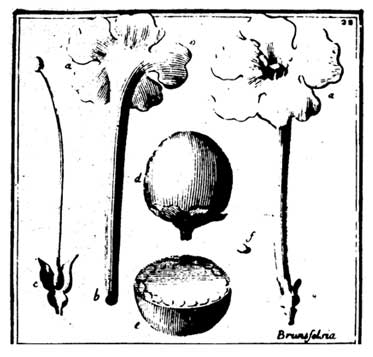
Brunfelsia is an erect, smooth shrub growing to a height
of 3 to 4 meters. Leaves are simple, green to yellowish-green, elliptic
to obovate, with entire margins, 5 to 10 centimeters long, pointed at both ends,
crowded on the ultimate twigs. Flowers are fragrant, terminal or axillary, solitary
or in pairs, shortly stalked, with five broad petals. Calyx is green, ovoid, 6
millimeters long and 5-toothed. Corolla tube is about 4.5 centimeters long, slender and
straw-colored; the limb is white to yellow, oblique and unequally 5-lobed,
about 5 centimeters in diameter. The fruit is rounded, about 1.5 centimeters in diameter,
with a yellow and somewhat fleshy pericarp and containing numerous seeds.
Distribution
- Recently introduced
to the Philippines.
- Cultivated in Manila and other large towns for ornamental purposes.
- Introduced from tropical America.
Constituents
- Phytochemical investigations have yielded steroids, flavonoids, tannins, and saponins.
- Yields normal fatty acids, and uncommon fatty acids such as ricinolic acid together with cyclopropenoids and normal fatty acids. (7) (5)
-
Traces of cyanide have been found the leaves, flowers, bark of stem and root. Alkaloids and chlorogenic acid have been reported from leaves and stems. (8)
- Phytochemical analysis of methanolic extract of leaves yielded steroids, flavonoids, tannins and saponins, with absence of alkaloids, terpenoids, anthraquinones and cardiac glycosides. Total phenolic content was 0.814±0.002.
(see study below) (4)
 Properties Properties
- Flowers emit a sweet scent with inebriating effects reminiscent of Brugmansia suaveolens. The fragrance emerges with the night and disappears with the dawn.
- Considered tonic, antioxidant, anti-diarrheal.
Parts used
- Fruit
- Propagated by stem cuttings.
Uses
Folkloric
- No recorded medicinal use in the Philippines.
- In Martinique, fruit is astringent, used
as a tonic; the syrup used for chronic diarrhea.
- In French Guiana, sugary fruit made into an astringent syrup for diarrhea.
- Used for snake bites, arthritis, syphilis.
Studies
• Cytotoxicity:
In a Bangladesh study evaluating the cytotoxicity activity 35 plant species
by the brine shrimp lethality bioassay, the methanolic extract of Brunfelsia
americana showed moderate cytotoxicity with LC50 less than 10.00 ug/ml. (2)
• Antioxidant: The presence of antioxidant activity was detected using TLC-DPPH screening. DPPH radical scavenging activity of the extract and standard ascorbic acid IC50 vales were 310 µg/ml and 200 µg/ml, respectively. Reducing power assay confirmed radical scavenging activity. Study showed high level of antioxidant activity in the plant. (see constituents above) (4)
• Unusual Fatty Acid in Seed Oil: Study of B. americana yielded ricinoleic acid together with cyclopropenoid and normal fatty acids. (5)
Availability
- Ornamental cultivation. |


 General
info
General
info  Properties
Properties

