|  Gen info Gen info
- Lablab purpureus is the only species in the monotypic genus Lablab.
Botany
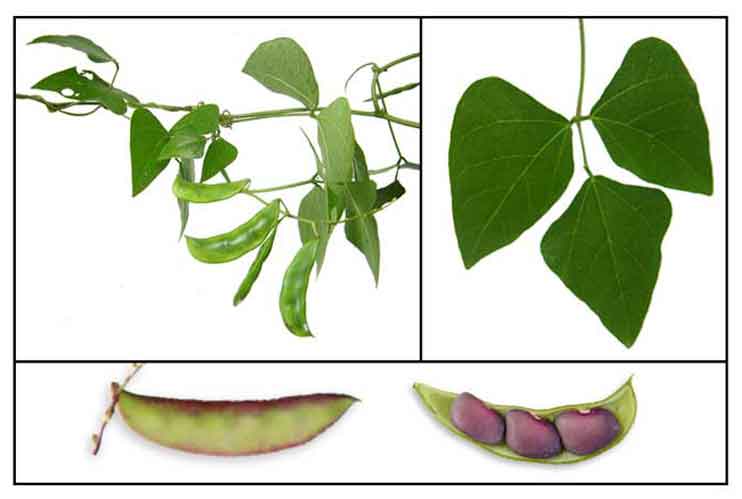
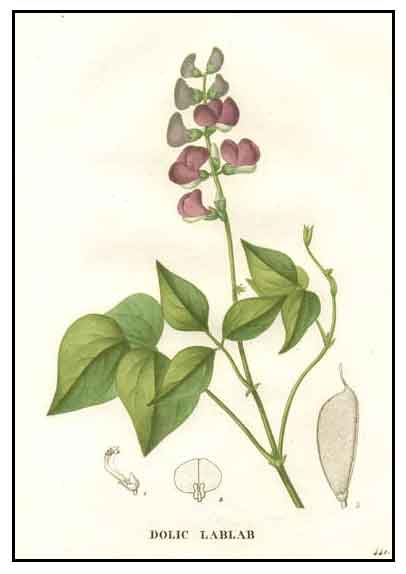
Bataw is a smooth, twining, climbing or trailing
vine, 4 to 6 meters long, often with smooth, usually purplish stems. Leaves are
long stalked, 3-foliate with in equilateral leaflets. Leaflets are entire, ovate, and 7 to 15 centimeters long.
Flowers are few to many, white to pink-purple in color, about 2 centimeters long, on erect, long peduncled racemes 15 to 25 centimeters long. Pods are oblong, flattened, purple-margined, flat, and elongated with a prominent
beak, about 7 to 12 centimeters long and 2 centimeters wide, containing 3 to 5 seeds.
 Distribution Distribution
- Introduced.
-
Commonly cultivated
throughout the settled areas in the Philippines.
- In some regions, naturalized.
- Now pantropic in cultivation.
Constituents
- Young pods are fairly good source of calcium and iron.
- Seeds yield protein, 23%; fat, 1.8%: ash, 3.5%; hydrocyanic acid, emulsin, allantoinase, and vitamin C1.
- Flowers yielded 6 flavonoids: luteolin (1), cosmosiin (2), leteolin-4^-0-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), luteolin-7-0-beta-D-glucopyranoside (4), rhoifolin (5), D-mannitol (6). (10)
- Yields protein, sucrose, maltodextrin, stachyose, glucose, raffinose, L-pipecolic acid, phytoagglutinin, phytin, calcium, phosphors, iron, pantothenic acid.
- Pod exudate showed it to consist of homologous fatty acids and their methyl esters—42 in all—from C-11 through C-24, including odd carbon chain compounds. The major constituents of the oil were trans-2-dodecenoic and trans-2-tetradecenoic acids. (12)
- Seed (fresh weight) yield: 334 calories per 100 g; water, 12.1%; Protein 21.5 g; fat 1.2 g; carbohydrate 61.4 g; fiber 6.8 g; ash 3.8 g; minerals: calcium 98 mg; phosphorus 345 mg; iron 3.9 mg. (20)
- Proximate analysis of seed powder yielded 8.47 ± 0.52% moisture; 3.50 ±0.07 ash, 1.02 ± 0.06% total fat, 23.95 ± 0.15 % total protein, 1.21 ± 0.16 total dietary fiber, 61.86 ± 0.70% total carbohydrate, and 354.4 ± 2.66 kcal/100 g energy. Major fatty composition (%) showed essential fatty acid linoleic acid 9,50 ± 0.68, linolenic acid 1.95 ± 0.18, palmitic acid 2.96 ± 0.18, stearic acid 0.77 ± 0.04, and oleic acid 1.10 ± 0.06. The major polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFA) present in seeds were essential omega-6 FA linoleic acid and omega-3 linolenic acid. (24)
- Phytochemical screening of methanol extract of aerial parts yielded the presence of saponins, tannins, alkaloids, and flavonoids. (see study below) (28)
 Properties Properties
- Considered tonic, febrifuge,
stomachic, antispasmodic.
- Boiled ripe seeds considered carminative.
- Seeds considered aphrodisiac, anthelmintic, antispasmodic, astringent, febrifuge and stomachic.
- Flowers considered emmenagogue.
- Studies have suggested antimicrobial, antihyperglycemic, hypolipidemic, antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, cytotoxic, anti-anemic, bioremediative, anti-asthma properties.
Propagation
- Propagation
by seeds.
-
Pods are harvested about
4 months after planting.
Toxicity concerns
- Mature, dried seeds are poisonous. Toxicity is attributed to high levels of cyanogenic glucosides. Cooking completely destroys the toxins: Boiling in two changes of water removes the toxins.
- Toxicity may manifest with weakness, vomiting, shortness of breath, twitching, stupor, and convulsions.
• Hepatorenal Toxicity (see study below) (25)
Parts used
Leaves, bean, roots.
Uses
Edibility / Nutritional
- Tender pods, seeds and
young leaves used as vegetable.
- Leaves are eaten raw or cooked.
- Flowers are eaten raw or steamed; used as salad ingredient.
- Roots can be boiled or baked.
- Tender young seed pods and immature seeds can be eaten raw or cooked.
-
Mature seeds are edible when thoroughly cooked.
(see toxicity concerns above)
- Seeds are used to make tofu and tempeh.
- Young leaves and pods are good sources of calcium, iron, vitamin C,
and other minerals.
 Folkloric Folkloric
- In Ilocos Sur, herbolarios use leaves to treat diarrhea and poultice of leaves to heal wounds.
-
Infusion of leaves used
for gonorrhea.
- Poultice of leaves for snake bites.
- Leaves used for menorrhagia and leucorrhea.
- Juice of the leaves mixed with lime, applied to tumors and abscesses.
- Salted juice from the pods used for ear inflammation and sore throat.
- Used as stomachic and antiseptic; given for abdominal pains, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- The Malays
make of poultice of the leaves mixed with rice-flowers and tumeric used
for eczema.
- In Indo-China,
Infusion of leaves for colic; flowers used as emmenagogue.
- Flowers prescribed for menorrhagia and leucorrhea.
- Seeds are considered aphrodisiac; also used to stop nose bleeds.
- In China, boiled ripe seeds used as tonic and carminative.
- Seeds used as febrifuge, stomachic, and antispasmodic.
-
In Bangladesh, the Santal tribe use wraps of crushed leaves around the throat for tonsillitis. Paste of leaves applied to skin diseases. The Garo tribal community take the seeds orally for low sperm count. In Odisha, India, seed paste is applied to scorpion stings. In Maharashtra, leaf juice is mixed with milk to cure arthritis. In Nepal, leaf juice and seeds used to relieve stomach ache. (28)
- In China, whole plant decoction used for alcoholic intoxication, cholera, diarrhea, globefish poisoning, gonorrhea, leucorrhea, menorrhagia, and dysentery. Stem used for cholera. Flower used for leucorrhea, menorrhagia, and dysentery. Fruit juice used for inflamed ears and throats. White seeds taken with vinegar for cholera and as anthelmintic, astringent, digestive and stomachic. (33)
Others
- Fodder: Plant is grazed or harvested for cut-and-carry systems, hay and silage. It can be mixed with other crops such as maize to make mixed fodder. (32)
- Ethnoveterinary: In Kenya, used to treat eye problems in sheep and lung problems in sheep, cattle, and goats. (32)
- Manure: As N-fixing legume, it is a valuable green manure. (32)
- Rituals: In Ilocos Sur, flowers represent love, fidelity, and longevity in courtship. Leaves used in Palm Sunday ceremonies to symbolize immortality. The early Tinguians of Abra consider the plant essential for travel through eternity. (33)
Studies
• Stem Cell Preservation
Factor: Stem
cell preservation factor FRIL (Flt3 receptor-interacting lectin), a
plant lectin extracted from Dolichos lablab was found to preserve hematopoietic
stems cells in vitro for a month.(1)
• Hypocholesterolemic:
Diet supplemented with D. lablab seeds showed a hypocholesterolemic
effect. (2)
• Cholecystokinin Secretion:
A peptide derived from dolicholin, a phaseolin-like protein from D lablab
potently stimulated cholecystokinin secretion from enteroendocrine STC-1
cells and suppressed food intake. (3)
• Antimicrobial / Antifungal:
n-Hexane and chloroform extracts of Dolichos lablab exhibited significant antimicrobial and antifungal activity against B subtilis, S aureus, P aeruginosa, E coli and C albicans. (4)
• Antidiabetic / Seeds:
Study evaluated the antidiabetic activity of a methanolic extract of D. lablab seeds in STZ-Nicotimamide induced diabetic model. Results showed dose-dependent reduction of blood glucose, total cholesterol, and triglycerides. (7)
• Anti-Inflammatory / Antioxidant / Cytotoxicity:
Study evaluated the in vitro anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and cytotoxic properties of methanol extracts of two Bangladesh bean pods, Lablab purpureus L. sweet 'white' and 'purple'. Results showed L. purpureus sweet 'white' and L. purpureus sweet 'purple' have significant anti-inflammatory activity as well as a potential source of natural antioxidants. L. purpureus sweet 'white' had concentration dependent potential cytotoxicity. (8)
• Effect on Iron Deficiency:
Study evaluated the effectiveness of D. lablab beans extracts against iron deficiency in rats. Results showed a significant increase in hemoglobin level. Standard drug used was ferrous sulfate. (9)
• Anti-Diabetic / Leaves: Study of ethanolic extract of leaves of D. lablab produced significant decrease of blood glucose level in alloxan-induced diabetes in rats. (11)
• Antihyperglycemic / Anti-Hyperlipidemic: Study evaluated the antihyperglycemic and antihyperlipidemic activity of a methanol extract of D. lablab. Results showed lowering of blood glucose, serum lipids and liver enzymes in diabetic rats. Standard drug was glibenclamide. (13)
• Natural Coagulants / Bioremediation: As natural coagulants, Moringa oleifera, Cicer arietinum, and Dolichos lablab significantly improved the removal of turbidity and total coliforms from synthetic raw water. The natural coagulants reduced 89-96% of total coliforms. (14)
• Effect in Iron Deficiency Anemia: Study evaluated the effect of Dolichos lablab (bataw) beans extract against iron deficiency in Wistar rats with induced anemia. Results showed a significant increase in hemoglobin level. (15)
• Natural Coagulants / Bioremediation of Water Turbidity: Study evaluated the efficacy of extracts of Dolichos lablab, Moringa oleifera and Cicer arietinum as natural coagulants for the clarification of water turbidity. The three test extracts showed significant efficacy in removing turbidity and total coliforms from synthetic raw water. (16)
• Galactoase- Specific Lectin / Seeds: Study isolated a galactose-specific lectin from the seeds of D. lablab. Among various sugars tested for inhibitory activity of the lectin, galactoase was found to be a potent inhibitor. Rabbit polyclonal antibody to the purified lectin specifically reacted with the lectin subunits in Western blot analysis. (17)
• Stem Cell Preservation: A plant lectin, stem cell preservation factor FRIL (Flt3 receptor-interacting lectin), was extracted from D. lablab and found to preserve hematopoietic stem cells in vitro. FRIL can also preserve neural progenitor cells in vitro by inhibiting both cell proliferation and differentiation. (18)
• Dolichin / Antifungal / Antiviral: An antifungal protein was modified from the seeds of Dolichos lablab. The protein, designated dolichin, exhibited antifungal activity against Fusarium oxysporum, Rhizoctonia solani, and Coprinus comatus. Dolichin was capable of inhibiting HIV reverse transcriptase and alpha- and beta-glucosidases which are glycohydrolases implicated i HIV infection. (19)
• Natural Coagulant / Antifungal / Antiviral: Study using locally available natural coagulants—Moringa oleifera, Cicer arietinum, Dolichos lablab—showed significant improvement in removing turbidity and total coiforms from synthetic raw water. (21)
• Anti-Asthma: Dolichos lablab has been reported to cause smooth muscle relaxant activity. (22)
• Hepatorenal Toxicity / Raw Seeds: Study investigated the influence of three varieties of seeds on hepatorenal antioxidant status in male Wistar rats. Results showed consumption of raw seeds induced hepatorenal toxicity in rats via induction of oxidative stress. There was significant elevation of serum marker enzymes along with increases in BUN and creatinine. (25)
• Antihyperglycemic / Antinociceptive / Beans: Study evaluated the antihyperglycemic and antinociceptive properties of a methanol extract of beans using OGTT and acetic-acid induced pain model in mice, respectively. Results showed dose-dependent and significant reductions in blood glucose levels in glucose-loaded mice. In antinociceptive testing, the extract reduced the number of abdominal constrictions. (27)
• Analgesic / Acute Toxicity Testing / Aerial Parts: Study evaluated the analgesic properties of aerial parts of L. purpureus. Acute toxicity testing of crude extract did not show any toxicity in mice at highest tested level of 3000 mg/kbw. Testing for analgesic activity showed dose-dependent and significant reductions in number of abdominal constrictions induced by IP administration of acetic acid. (28)
• Anti-Obesity / CS-IVA / Seeds: Previous study reported Dolichos lablab extract inhibited high-fat diet induced increases in body weight and body fat mass and ameliorated increases in body weight. This study evaluated the molecular mechanism for the inhibitory effect of DLL extract or Chikusetsusaponin IVa (CS-IVa) isolated from the seed extract. Study showed both DLL-Ex and CS-IVa have potent inhibitory activity on adipocyte differentiation. Results suggest a potential for DLL and CS-IVa as a functional food material to treat obesity. (29)
• Hematological Benefit / Potential Iron Source: Study evaluated the effectiveness of D. lablab beans extract against iron deficiency in rats. Anemia was induced by tail clipping. Results showed significant increase in hemoglobin level from 11.33 to 14.33 while hematocrit increased from 34.0 to 43.0 after 14 days of treatment. (30)
• Sedative / Anxiolytic / Seeds: Study evluated crude methanolic seed extract of Lablab purpureus for sedative effect using open field and hole cross test, and anxiolytic effect using
elevated plus maze (EPM) test. Results showed dose dependent suppression of motor activity and exploratory behavior in open field and hole cross test, and significant (p<0.01) increased exploration to time spent in EPM open arms. (31)
• Anticoagulant / Fibrinogenolytic / Anti-Platelet Aggregation / Seeds: Study evaluated the anticoagulant, fibrinogenolytic and anti-platelet aggregation activities of L. purpureus seed radicle extract.
The LPRE significantly increased plasma clotting time and inhibited platelet aggregation induced by agonist adenosine diphosphate (ADP). (35)
• Accelerated Wound Healing / Hydrogel Formulation: Study evaluated the healing effect of D. lablab extract hydrogel on full-thickness wounds in male albino Wistar rats. Results showed potent wound healing ability, evidenced by improved wound closure and tissue regeneration, and histopathological parameters. There was increased skin hydroxyproline level, antioxidant potential, wound contraction, and anti-inflammatory activity by modulation of production of cytokines TNF-α, IL-1ß, and IL-6.
(36)
Availability
Cultivated for market
produce.
Wildcrafted.
|


 Gen info
Gen info Distribution
Distribution



