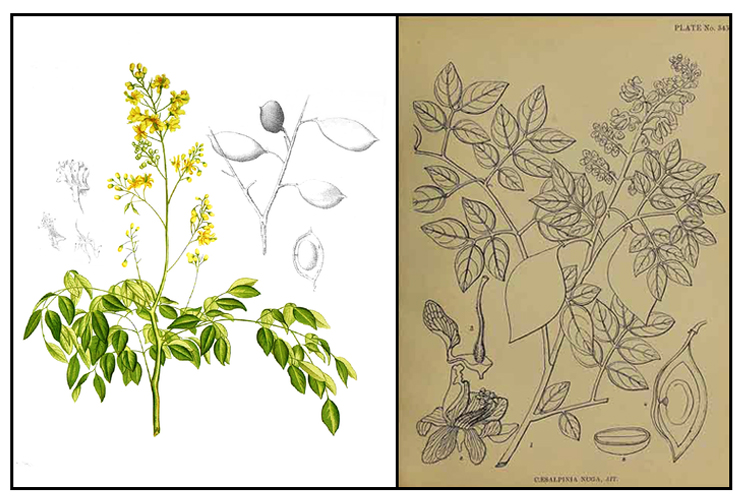
 Botany Botany
Bakaig is a smooth, climbing shrub reaching a length of 10 meters or more. Branches are armed with short, stout, hard, hooked prickles. Leaves are bipinnate, 20 to 30 centimeters long, and the rachis armed with recurved spines beneath. Pinnae are 6 to 8, and rather distant. Leaflets are 4 to 6 on each pinna, leathery, shining, ovate to elliptic-ovate, 2 to 5 centimeters long, and pointed at the tip. Flowers are yellow, borne in terminal and ample panicles, and about 1 centimeter in diameter. Pod is 4 to 5 centimeters long, 2.5 to 3 centimeters wide, beaked, hard, and indehiscent, and contains a single seed.
Distribution
- Throughout the Philippines in tidal swamps, in thickets along the seashore, etc.
- Pantropic.
 Constituents Constituents
- Study of stems and roots of C. crista yielded nine new cassane-type diterpenes, taepeenin A-I, and two new norcassane-type diterpenes, nortaepeenin A-B, along with three known diterpenes, vinhaticoic acid, methyl vinhaticfoate and taepeenin A. (5)
- Leaf extracts yielded phenolic acids viz., gallic, protocatechuic, gentisic, chlorogenic, caffeic, p-coumaric and ferulic acids. (see study below)
(7)
- Ethanolic seed extract yielded flavonoids, alkaloids, tannins, triterpenoids, coumarin glycosides, and proteins.
(12)
- Seed kernel extracts yielded five new cassane-type diterpenes, caesalpinins MA-ME (1-5), and three new norcassane-type diterpenes, norcaesalpinins MA-MC (6-8), together with 12 known cassane type diterpenes: 14(17)-dehydrocaesalmin F, caesaldekarin e, caesalmin B, caesalmin C, caesalmin E, 2-acetoxy-3-deacetoxycaesaldekarin e, 2-acetoxycaesaldekarin e, caesalpinin C, 7-acetoxybonducellpin C, caesalpinin E, norcaesalpinin B, and 6-acetoxy-3-deacetoxycaesaldekarin e. (15)
- A methanolic extract yielded two novel compounds, 2-hydroxytrideca-3,6-dienyl-pentanoate and octacosa-12,15-diene along with known compounds 3-O-methylellagic acid 3′O-α-rhamnopyranoside, β-sitosterol and sucrose. (see study below)
(22)
Properties
- Roots considered diuretic, tonic, anticalculous.
- Seeds considered antiperiodic, tonic, febrifuge, antidiarrheal.
- Bark considered antiperiodic, rubefacient.
- Studies have suggested anthelmintic, anti-amyloidgenic, antiviral, antibacterial, hepatoprotective, analgesic, anti-inflammatory, nootropic, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-fasciolic, anticoagulnt, antiplatelet properties.
Parts used
Seeds, leaves, fruit.
Uses
Folkloric
- In the Philippines, decoction from crushed seeds used as emetic and for dysentery.
-
In India, roots employed as diuretic and used for cases with stone or gravel in the bladder.
- Root juice used orally and externally as application for ophthalmia.
- Externally and internally the juice of the stem used for eye diseases. Roasted fruit also used for the same purpose.
- Finely powdered leaves used as uterine tonic for women immediately after delivery.
- In Ayurveda used for gynecologic diseases, piles, ulcers, worms and deranged kapha. Balances all the tridoshas: vata, pitta and kapha doshas. (26)
- In India, oil from the seed used to soften the skin and remove pimples. Bark used for toothaches. Used for colic, convulsions, malaria, tuberculosis, leprosy and palsy. Also used as uterine stimulant and for cleansing the uterus. (9)
Others
- Ritual / Decorative: In India, seeds used as jewelry, prayer beads, good luck charms and worry stones. (24)
Studies
• Anthelmintic: Study evaluated the anthelmintic activity of Chenopodium
album (L.) and Caesalpinia crista (L.) against trichostrongylid nematodes
of sheep: Study showed both C. crista and C. ablum possess
anthelmintic activity in vitro and in vivo, supporting its traditional use in Pakistan. (2) Study of leaves showed anthelmintic activity in naturally infested goats with strongyles. C. crista also showed activity against Ascaridia galli in vitro. Study also reviewed the anthelmintic efficacy of C. crista seeds in various models of experimentally induced helminthiasis. (24)
• Anti-Amyloidogenic / Alzheimer's Disease: Abeta (amyloid beta) is a major etiological factor in Alzheimer's disease. Study showed C. crista aqueous extract could inhibit the Abeta(42) aggregation from monomers and oligomers and able to disintegrate the preformed fibrils. (3)
• Nootropic / Memory Enhancer / Seeds: Study evaluated the potential of dried seed kernels of C. crista extract as a learning and memory enhancer. Results suggest CC can be beneficial in improving cognition in disorders like dementia and other neurodegenerative disorders. (4)
• Antioxidant / Leaves: A 70% methanol extract of C. crista leaves showed antioxidant and ROS scavenging, attributed to phenolic and flavonoid compounds. (6)
• Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory / Leaves: Study evaluated the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of C. asiatica and C. crista leaf extracts. Both exhibited antioxidant properties and inhibited 5-lipoxygenase (anti-inflammatory) in a dose dependent manner, with C. crista showing better activities than C. asiatica, attributed to the higher gallic acid and ferulic acid content. (7)
• Hepatoprotective / Iron-Overload Liver Toxicity: Study evaluated the ameliorating effect of C. crista extract on iron-overload-induced liver injury in mice. Treatment showed attenuation of percentage increase in liver iron and serum ferritin levels. CCME also showed a dose-dependent inhibition of lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation and liver fibrosis. The hepatoprotective effect against the iron overload was attributed to its potent antioxidant and iron-chelating property. (8)
• Antidiabetic / Seeds: Study evaluated the antidiabetic activity of ethanolic and aqueous seed extracts of Caesalpinia crista in STZ-induced diabetic 2-day old pups model. Results showed antidiabetic effects, with the aqueous extract showing more significant effect than the ethanolic extract. Histopath studies showed regeneration of ß-cells of the pancreas. (10)
• Anticancer / Root Bark: Study evaluated the possible anticancer activity of an alcoholic root bark of Caesalpinia crista against Ehrlich Ascites Carcinoma (EAC) Tumor model. Results showed increased survival time and life span, together with significant reduction of solid tumor mass. (11)
• Analgesic / Antioxidant / Anti-Inflammatory / Seeds: Study of an ethanolic seed extract of C. crista showed potent antioxidant activity by DPPH assay, significant anti-inflammatory activity by Carrageenan induced paw edema with diclofenac as standard, and potent analgesic activity by writhing reflexes and tail withdrawal latency in mice. (12)
• Antipyretic / Seeds: Study evaluated the antipyretic activity of ethanolic and aqueous extracts of seeds using Brewer's yeast induced pyrexia in various experimental animal models. Results showed antipyretic action attributed to the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. The ethanolic extract showed more significant activity than the aqueous extract. (13)
• Antimicrobial / Seeds: Study showed seed extracts of Caesalpinia crista to have antimicrobial activity against seven of eight selected strains of bacteria and fungi, showing maximum inhibitory effect on P. aeruginosa and F. oxysporum. (14)
• Antimalarial / Antiplasmodial / Seeds: Study evaluated 44 cassane- and norcassane-type diterpenes isolated from C. crista of Mayanmar and Indonesia for antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falcifarum clone in vitro. Most of the tested diterpenes displayed antimalarial activity, with norcaesalpinin E showing the most potent activity with an IC50 of 0.090 µM, more potent than the drug chloroquine. (16)
• Seed Oil / Commerce Potential: Study of shade dried oil yielded total 19.66% saturated fatty acids and 80.33% unsaturated fatty acids. Physiochemical analysis revealed a non-drying oil. Results suggest a potential for use in preparation of liquid soap, hair shampoos, and value added products. (17)
• Hepatoprotective Against Iron Load-Induced Toxicity: Study evaluated the ameliorating effect of C. crista extract on iron overload-induced liver injury. Results showed a dose-dependent inhibition of lipid peroxidation, protein oxidation, and liver fibrosis. Study confirmed the hepatoprotective effect likely related to its potent antioxidant and iron-chelating property. (19)
• Antiviral Against Against Poultry Viruses: Various extracts of lathakaranja showed complete inhibition of paramyxovirus while showing highly significant inhibitory activity on orthomyxovirus. Study concludes the medicinal plant C. crista might be useful against economically important viral pathogens of poultry birds. (20)
• Anthelmintic / Seeds: Study evaluated crude seed extracts of Caesalpinia crista for anthelmintic activity against Pheretima posthuma and Ascardia galli. Results showed all extracts significantly demonstrated paralysis and death of worms at higher concentration 15% w/v compared to standard drug piperazine citrate. (21)
• Antibacterial / Seeds: A methanolic extract yielded two novel compounds, 2-hydroxytrideca-3,6-dienyl-pentanoate and octacosa-12,15-diene along with known compounds. The isolated compounds, extract and fractions showed significant in vitro antibacterial activity against S. aureus and MRSA. (see constituents above) (22)
• Toxicity Studies / Seeds: Study evaluated the acute and sub-acute toxicity of ethanol extract of seeds of Caesalpinia crista in albino mice. On acute toxicity study the limit test dose by OECD guidelines was 2000 mg/kg and for sub-acute toxicity, doses of 200 mg/kg and 400 mg/kg per day for 28 days. No toxic effects and no mortality were recorded for the study. Results showed use of the seed extract is safe. (23)
• Anti-Ulcer / Seeds: Study evaluated the anti-ulcer activity of various extracts of Caesalpinia crista seeds on pylorus ligation and indomethacin-induced gastric lesions in albino rats.
Results showed decrease in ulcer score and ulcer index. The ethanol extract showed maximum effect at 200 mg/kbw. (25)
• Hepatoprotective / Paracetamol Induced Toxicity: Study investigated the hepatoprotective activity of C. crista ethanol extract of leaves against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Results showed significant reduction of elevated serum marker enzymes, bilirubin and triglycerides at 200 mg/kbw and 400 mg/kbw extract doses. (27)
• Cytotoxicity / Bark: Study of methanolic extract of barks of Caesalpinia crista for cytotoxic activity by Brine Shrimp Lethality Bioassay showed significant cytotoxic activity with LC50 of 9.10 µg/ml. Chloramphenicol was used as reference with LC50 of 10µg/ml. (28)
• Inhibition of Cholinesterase and ß-Amyloid Aggregation / Potential for Alzheimer's Disease: Study evaluated leaves extract fractions for cholinergic and anti-amyloidogenic activities for treatment of Alzheimer's disease. A methanol extract showed antioxidant property and inhibition of cholinergic enzymes acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase. In anti-amyloidogenic evaluation, the CCMeOH showed potential for inhibition of oligomers, fibrillation of Aß42 with good defibrillation of amyloid cascading properties. Results suggest a promising option for treatment of Alzheimer's disease. (29)
• Protection against DNA and Membrane Damage / Leaves: Study evaluated C. crista leaves against free radical induced DNA and erythrocyte damage using H2O2 as oxidative agent. Leaf ethyl acetate (EA) extract yielded a total polyphenol content of 94.5 ± 3.8 mg/g GAE, while a methanol extract yielded 52.7 ± 2.8 mg/g GAE and a water extract yielded 31.84 ± 1.8 mg/g GAE. Total flavonoid content was highest in the EA extract at 60.46 ± 2.3 mg/g QE. Among the extracts, EA and ME showed better protection against RBC hemolysis and DNA damage. Results suggest C. crista contains biomolecules and can inhibit oxidative stress. (31)
• Antiplasmodial / Acute Toxicity Study / Seeds: Study evaluated the antiplasmodial activity of C. crista seed extracts against rodent malarial infections in chloroquine sensitive Plasmodium falcifarum strain. Results showed significant (p<0.05) and dose-dependent decrease in parasitaemia in varying doses of 50-200 mg/kg p.o. in both suppressive and curative tests. The alcoholic extract showed no toxicity in Wistar rats. Oral LD50 was greater than 5000 mg/kg. .(31)
• Anticoagulant / Antiplatelet / Seeds: Study evaluated the anticoagulant, antiplatelet, and clot lysis efficiency of C. crista seed aqueous extract. The extract showed strong anticoagulant effect as evidenced by enhanced clotting time. The extract also exhibited strong antiplatelet activity by inhibition of both ADP and epinephrine agonists induced platelet function. The extract exhibited no damaging effects on blood vessels, edema, and RBC lysis potency. (32)
• Anti-Fasciolic Efficacy in Infected Buffaloes / Seeds: Study evaluated the efficacy of C. crista seeds and Saussurea lappa roots to treat buffaloes naturally infected with fasciolosis, with efficacy compared with triclabendazole. The two plants were found significantly effective (p<0.05) and safe to use against fasciolosis. Effficacy for triclabendazole was 100% after the first dose while the two herbal treatments required a second dose of 150 mg/kbw. The antifasciolic effects may be due to the presence of metabolites like alkaloids, tannins, saponins, phenolic compounds, and flavonoids. (33)
• α-Caesalpin / Antidiabetic / In Silico Docking Analysis / Seed: Study evaluated the bioactivity of α-caesalpin compound from C. crista for antidiabetic-based on reverse docking studies.. Results showed α-caesalpin has greater potential as antidiabetic based on its binding affinity and intermolecular interactions. AMES test showed the α-caesalpin is not a potential mutagens and not carcinogenic. Druglikeness prediction showed α-caesalpin fulfills the requirements with 0.55 bioavailability score. (34)
Availability
Wild-crafted. |

![]()



 Botany
Botany Constituents
Constituents